確率システム (Probabilistic Systems)
自己位置推定と検証
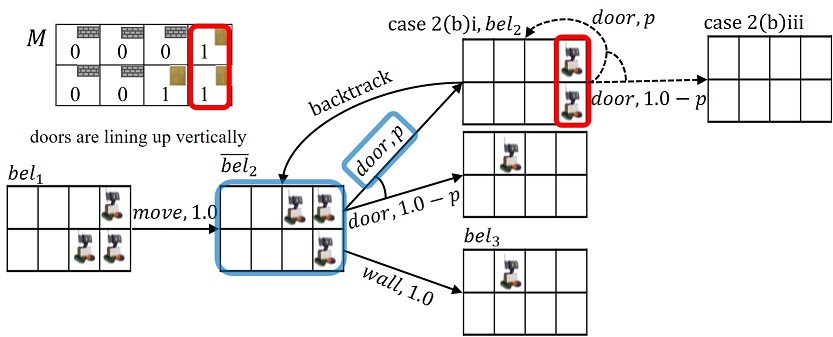
In robotics, self-localization often plays an important role, using values obtained by observations of an external environment. A simple example is a robot running on a maze, where the robot doesn't know its initial position. For such a case, it is necessary to design movements, since estimation depends on arrangement of structures on a map. We fix movements of the robot. We then verify using a probabilistic model checker PRISM, to see whether the robot can determine its position for a given map.
- Ryo Watanabe, Kozo Okano, and Toshifusa Sekizawa: "Towards Verification of Robot Design for Self-localization," Thirteenth Haifa Verification Conference (HVC 2017), LNCS, Vol. 10629, pp. 245-248, 2017.
- Toshifusa Sekizawa, Taiju Mikoshi, Masataka Nagura, Ryo Watanabe, Qian Chen: "Probabilistic Position Estimation and Model Checking for Resource-Constrained IoT Devices," Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Computer Communication and Networks (ICCCN 2018) pp. 1-7, 2018, IEEE.
自律移動ロボットの振舞い検証 (Behavior Verification of an Autonomous Robot)